
32
Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012 Aug;69(15):2593-608.
Mesenchymal stem cells and neural crest stem cells
from adult bone marrow: characterization of their
surprising similarities and diferences.
Wislet-Gendebien S, Laudet E, Neirinckx V, Alix P, Leprince P, Glejzer A, Poulet C, Hennuy B,
Sommer L, Shakhova O, Rogister B.
Abstract
The generation of neuronal cells from stem cells obtained from adult bone marrow is of
signifcant clinical interest in order to design new cell therapy protocols for several neuro-
logical disorders. The recent identifcation in adult bone marrow of stem cells derived from
the neural crest stem cells (NCSC) might explain the neuronal phenotypic plasticity shown
by bone marrow cells. However, little information is available about the nature of these
cells compared to mesenchymal stem cells (MSC), including their similarities and diferences.
In this paper, using transcriptomic as well as proteomic technologies, we compared NCSC
to MSC and stromal nestin-positive cells, all of them isolated from adult bone marrow. We
demonstrated that the nestin-positive cell population, which was the frst to be described
as able to diferentiate into functional neurons, was a mixed population of NCSC and MSC.
More interestingly, we demonstrated that MSC shared with NCSC the same ability to truly
diferentiate into Tuj1-positive cells when co-cultivated with paraformaldehyde-fxed cere-
bellar granule neurons. Altogether, those results suggest that both NCSC and MSC can be
considered as important tools for cellular therapies in order to replace neurons in various
neurological diseases.
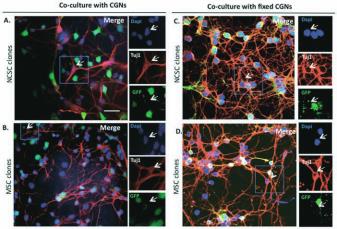
Neuronal characteristics of NCSC and MSC clones.
NCSC and MSC clones were co‐cultured for 5 days with green fuorescent protein (GFP)–positive cere-
bellar granule neurons (CGNs, green). Interestingly, both sets of clones were able to diferentiate into
Tuj1-positive cells (red, A and B). Arrowheads show clonal cells that were Tuj1-psoitive (red), but GFP-
negative (green) rejecting their CGNs origin. To determine if the presence of Tuj1-positive cells from MSC
clones co-cultivated with CGNs, was due to cell fusion events or because of other requested factors
expressed by CGNs, we co-cultivated NCSC clones and MSC clones with CGNs that have been cultiva-
ted for 5 days before being fxed with 4 % paraformaldehyde. Clones were cultivated on top of fxed
CGNs in presence of CGNs conditioned medium for 7 days. Interestingly, we were still able to obtained
Tuj1-positive cells with both NCSC and MSC, in those conditions (C,D). Nuclei were counterstained with
Dapi (blue). Scale bars =30 μm.